The majority of lists containing SEO optimal guidelines are jam-packed with poor, outdated advice. Either that, or they concentrate on aspects that only apply to a small portion of readers.
In other words, they consist of SEO tips, rather than optimal guidelines.
Optimal guidelines should be followed by everyone, regardless of whether you operate a blog, ecommerce store, or local brick and mortar store.
In today's post, we're going to cover the most crucial optimal guidelines to implement for each page on your site.
New to SEO? Check out our
HTTPS enhances the security of your site's pages by encrypting the information exchanged between the visitor and server. It has been one of Google's ranking factors since 2014.
You can determine if your site is already using HTTPS by checking the loading bar in your browser.
If there is a lock icon preceding the URL, then you are good.


If not, you will need to install an SSL certificate.
Many web hosts offer these as part of their packages. If your web host does not, you can acquire a free one from LetsEncrypt.
The good news is that switching to HTTPS is a one-time job. Once installed, every page on your site will be secure, including future published pages.
2. Ensure your pages load quickly
Nobody wants to visit a page that takes an eternity to load. This is why page speed has been a ranking factor for desktop since 2010 and for mobile since 2018.
Several factors impact page speed, including your site's code, server location, and images.
You can get a general sense of your pages' performance by using Google's Pagespeed Insights tool. Simply enter a URL, and you will see a score between 0-100, followed by improvement suggestions.
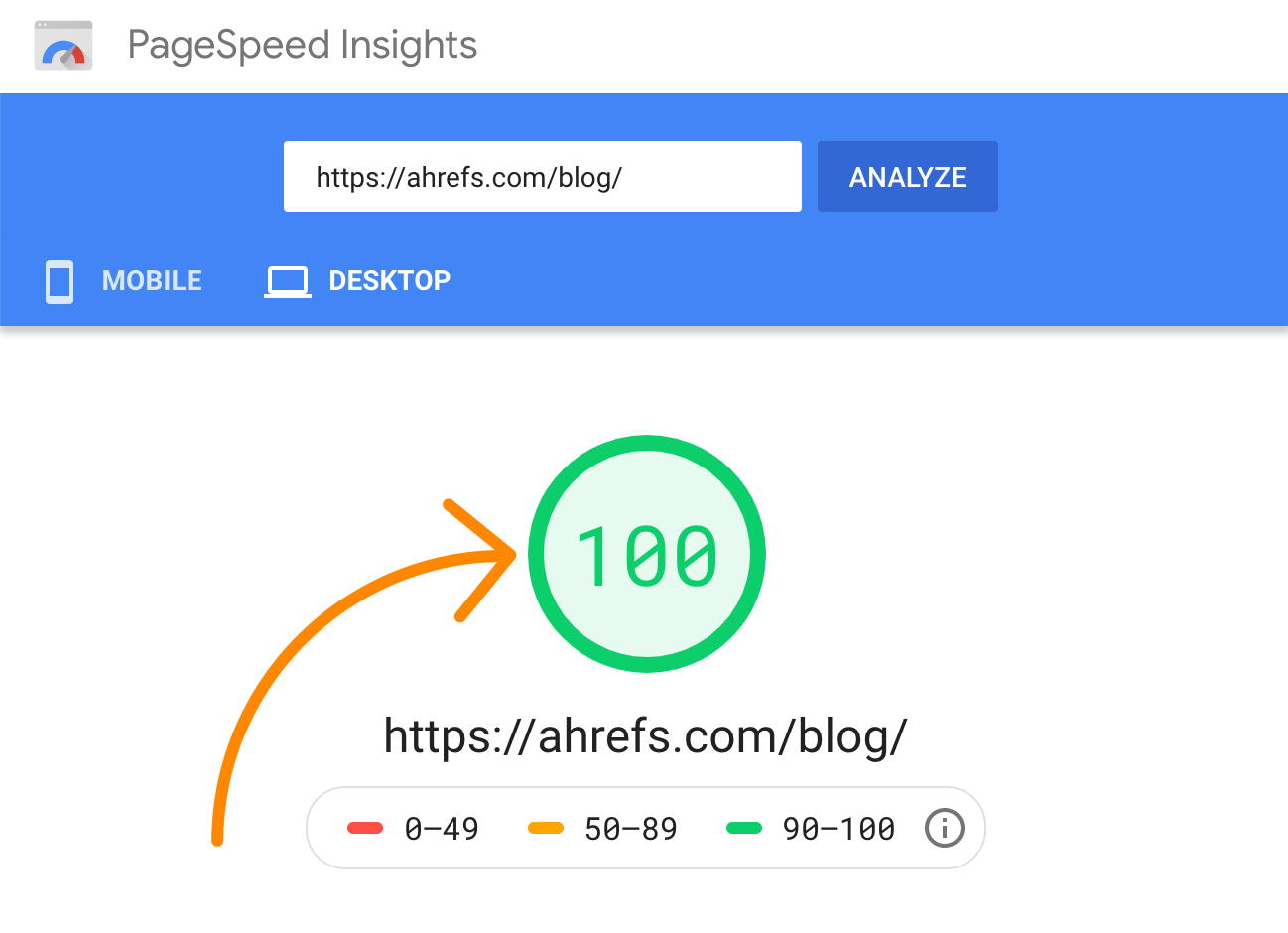

The challenge with Pagespeed Insights is that you can only test one page at a time.
You can resolve this by signing up for Google Search Console and checking the Speed report. This report shows you which pages are loading slowly on desktop and mobile, and provides insights into the reasons behind it.
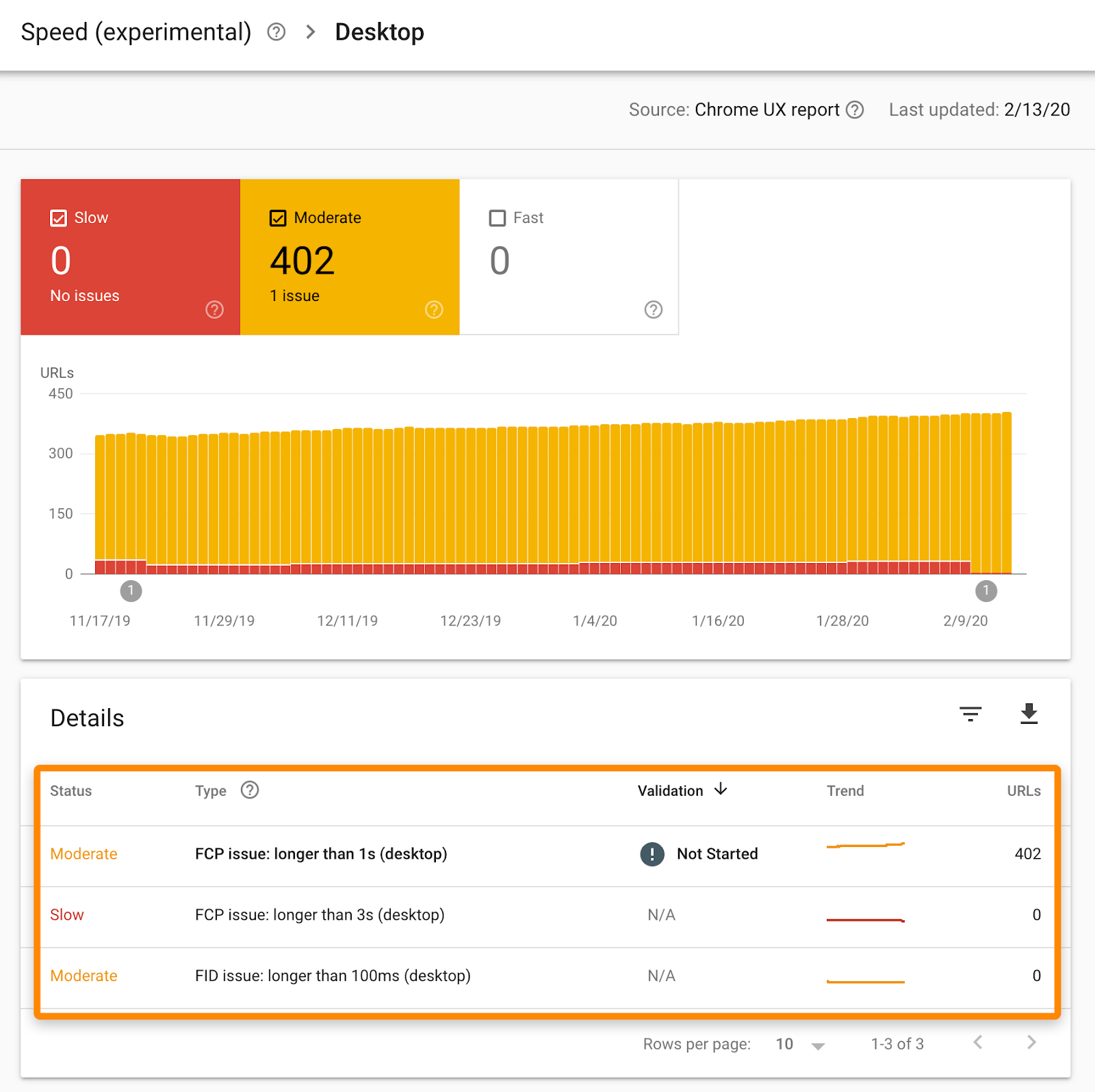

Some of these issues can be complex, so it is best to consult with a developer or technical SEO expert to address them.
Here are some general tips to ensure fast-loading pages:
- Utilize a CDN. Most websites are hosted on a single server in one location. As a result, data must travel long distances for some visitors before it is displayed in their browsers. This causes slow loading. CDNs resolve this by serving critical resources like images from a network of servers worldwide, resulting in faster local loading of resources.
- Compress images. Image files are large, which leads to slow loading. Compressing images reduces file size, resulting in faster loading times. However, it is important to find the right balance between size reduction and image quality.
- Implement lazy-loading. Lazy-loading defers the loading of offscreen resources until they are needed. This means that the browser does not need to load all images on a page before it becomes usable.
- Select an optimized theme. Choose a well-optimized website theme with efficient code. Test the theme demo using Google's Pagespeed Insights tool to evaluate its performance.
3. Focus on a subject with 'search traffic potential'
Keyword research is a vital component of SEO. There is no point in investing time, effort, and money to rank for things that nobody is searching for (unless you solely aim to attract backlinks).
For instance, suppose you sell software tutorials. It would be pointless to target a keyword like "how do i make the font larger in coffee cup html editor" because it has zero search volume.…
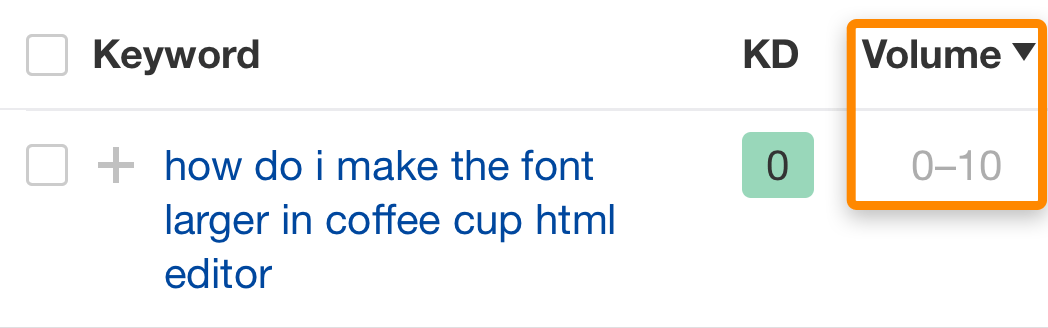

.… and the top-ranking page does not generate any organic traffic:
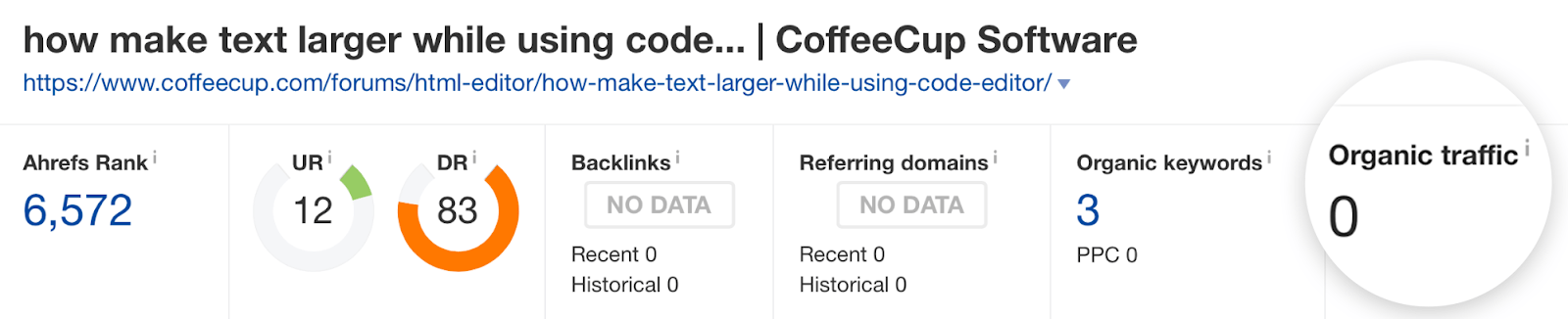

While search volume can indicate traffic potential for a keyword, it can also be misleading.
Consider these two keywords:
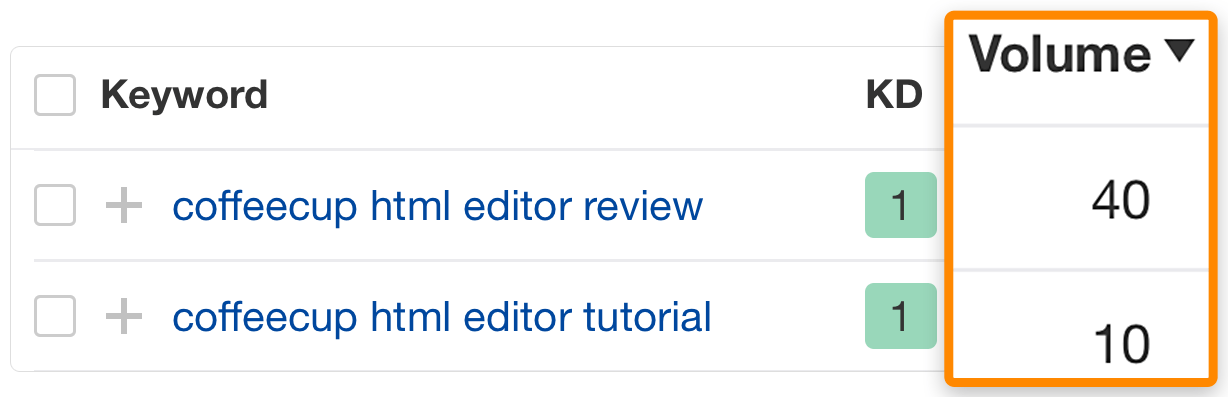

The former keyword has a higher monthly search volume, but the top-ranking result only receives an estimated 65 monthly organic visits in the US…
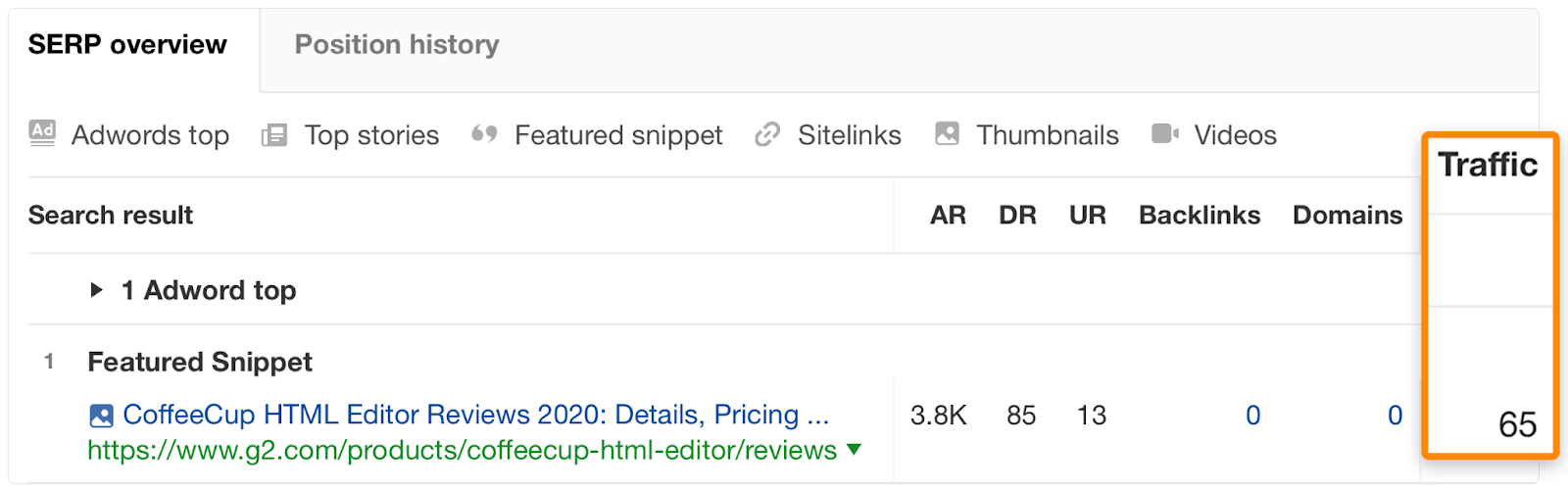

… compared to 191 visits to the page ranking first for the lower volume keyword:
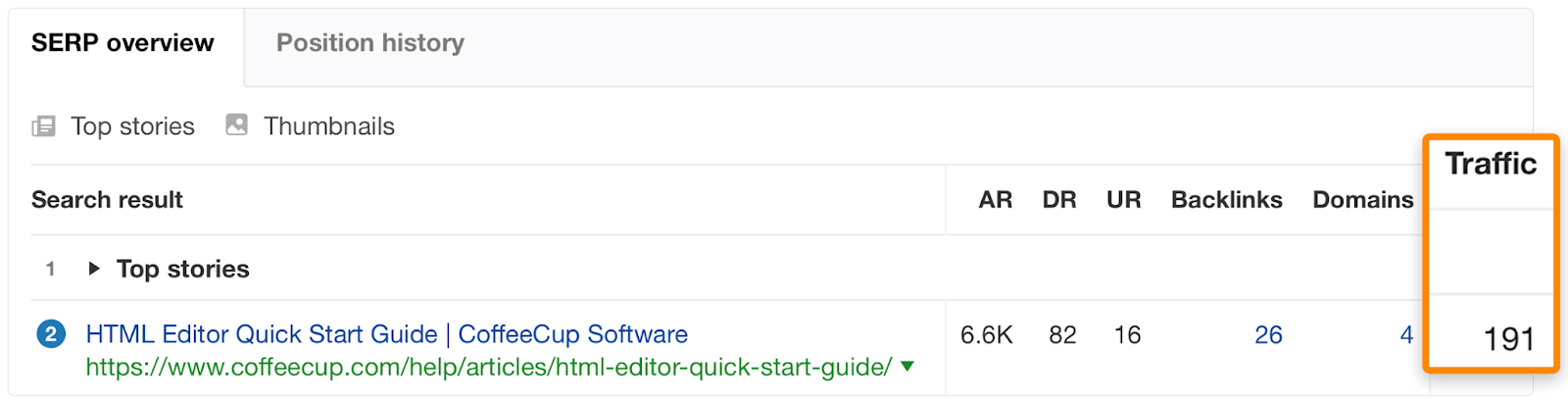

This disparity occurs because the page ranking for the lower volume keyword is a part of a broader topic and receives traffic from other keywords.
In other words, more people are searching for a coffee cup tutorial than a coffee cup review.
Thus, while search volume is a useful filter for keyword ideas, it is crucial to analyze estimated traffic to the top-ranking pages to gain a better understanding of true traffic potential.
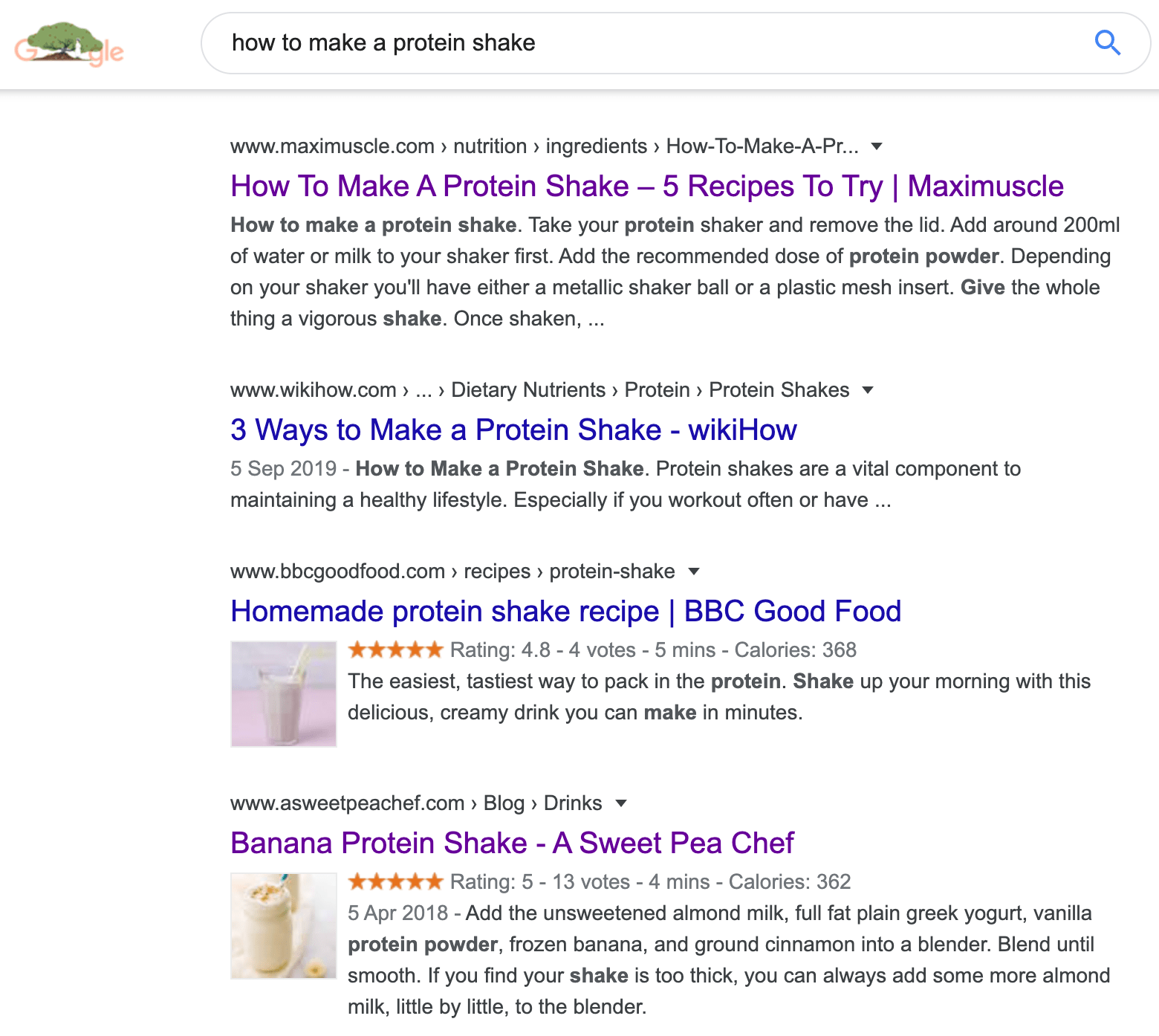
Nobody wants to see product pages in the search results for "how to make a protein shake."
Those individuals are in learning mode, not buying mode.
Google understands this, which is why all the top results are blog posts, not pages selling protein powder.

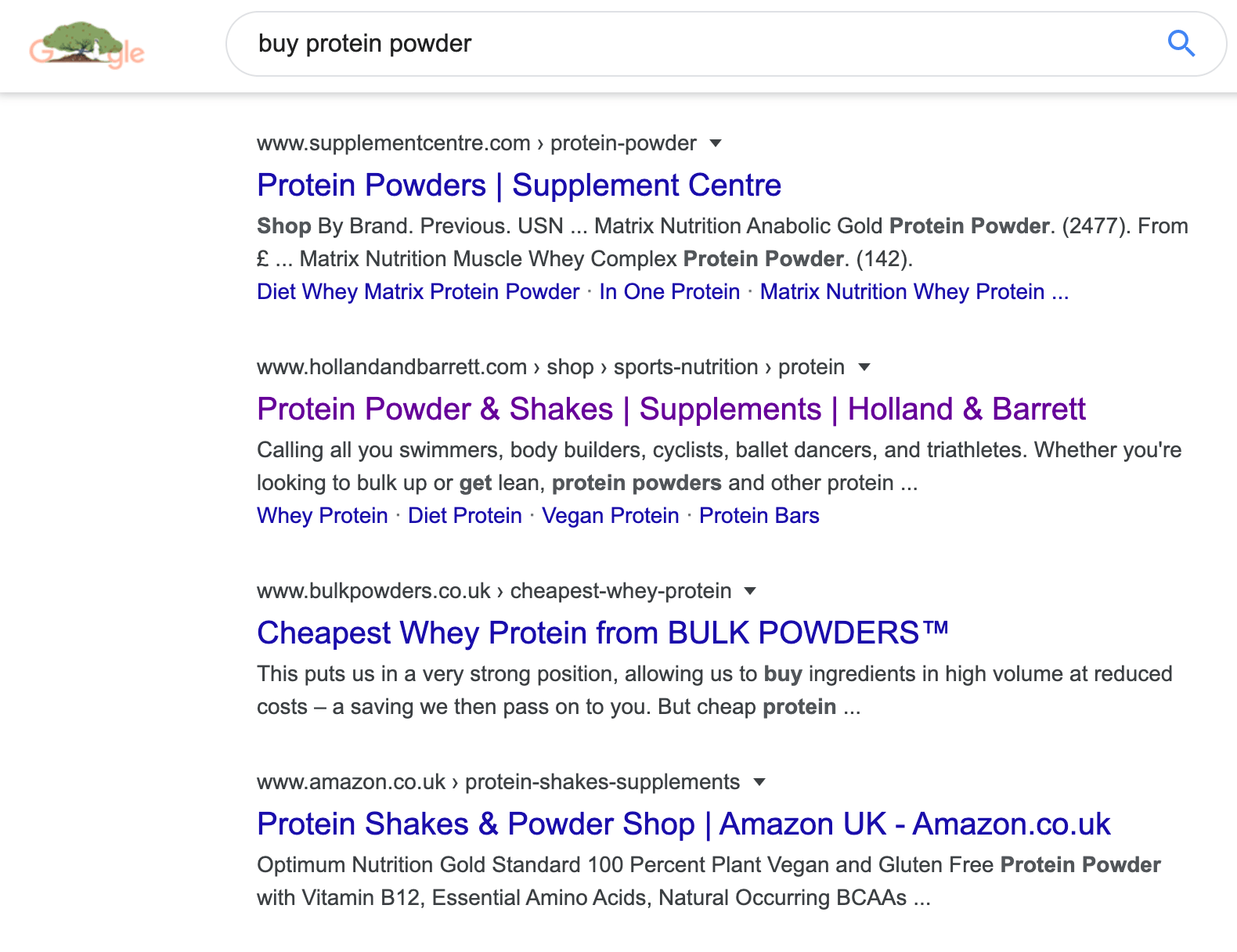
The opposite is true for a query like "buy protein powder."
Individuals searching for that query are not looking for a protein shake recipe; they want to purchase protein powder. Consequently, the majority of the top 10 results consist of ecommerce category pages, not blog posts.

Examining Google's top results in this manner provides insight into the intent behind a query, enabling you to determine the type of content necessary to rank.
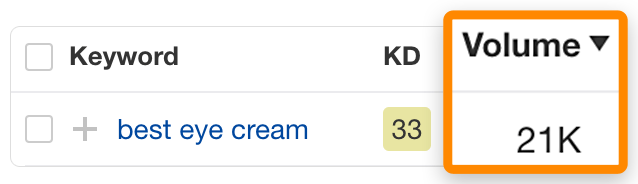
Let's examine a less obvious keyword like "best eye cream," which receives an estimated 21k monthly searches in the US.

An eye cream retailer might assume that it makes perfect sense to rank a product page for this keyword. However, the search results present a different story:
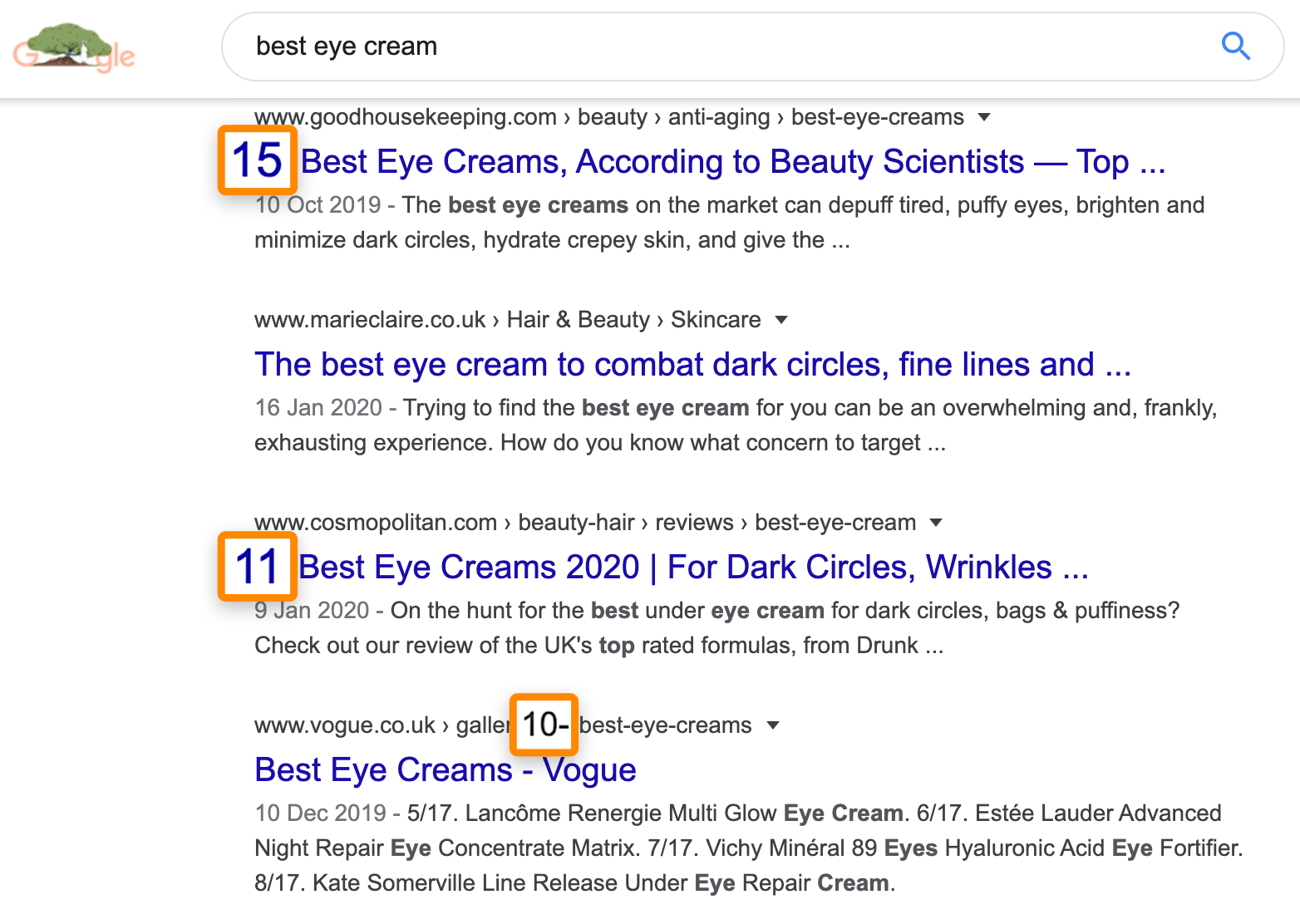

Almost all the results consist of list-style blog posts, not product pages.
To have any chance of ranking for this keyword, you would need to follow suit.
Catering to search intent goes beyond creating a specific type of content. You also need to consider the content format and angle.
Learn more about this in our guide to optimizing for search intent.
5. Focus on a subject within your area of expertise
Competitive keywords are often dominated by large brands with extensive backlink profiles and substantial resources.
For example, examine the number of referring domains to the pages ranking for "best credit card":
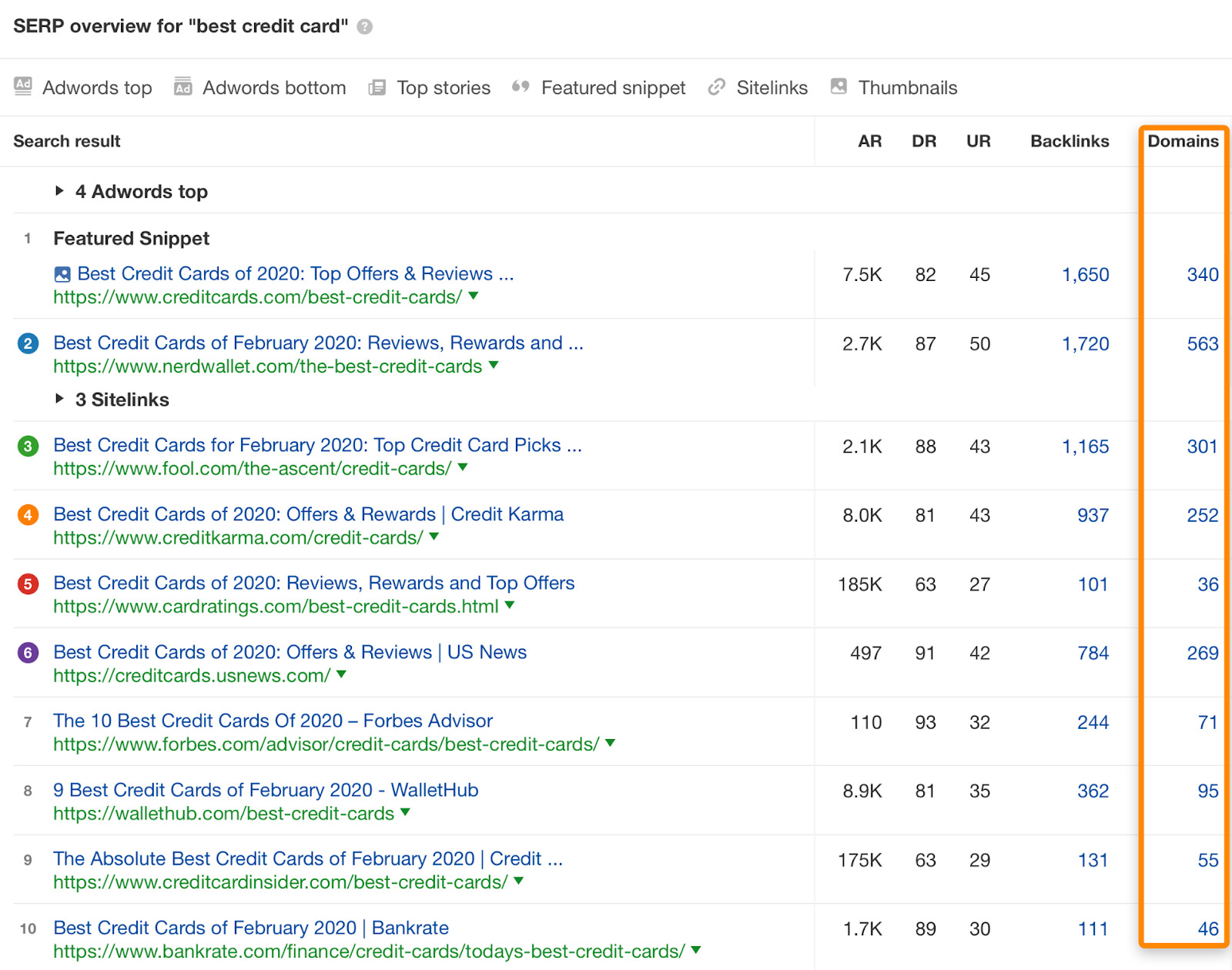

These results are dominated by big players like NerdWallet, Credit Karma, and CreditCards.com, and the average number of referring domains to the top five results is over 300.
Ranking for this keyword in the short-to-medium term would be nearly impossible for 99% of individuals.
That is why it is beneficial to target keywords within your area of expertise.
In this case, that may involve keywords like "best credit cards for lounge access":
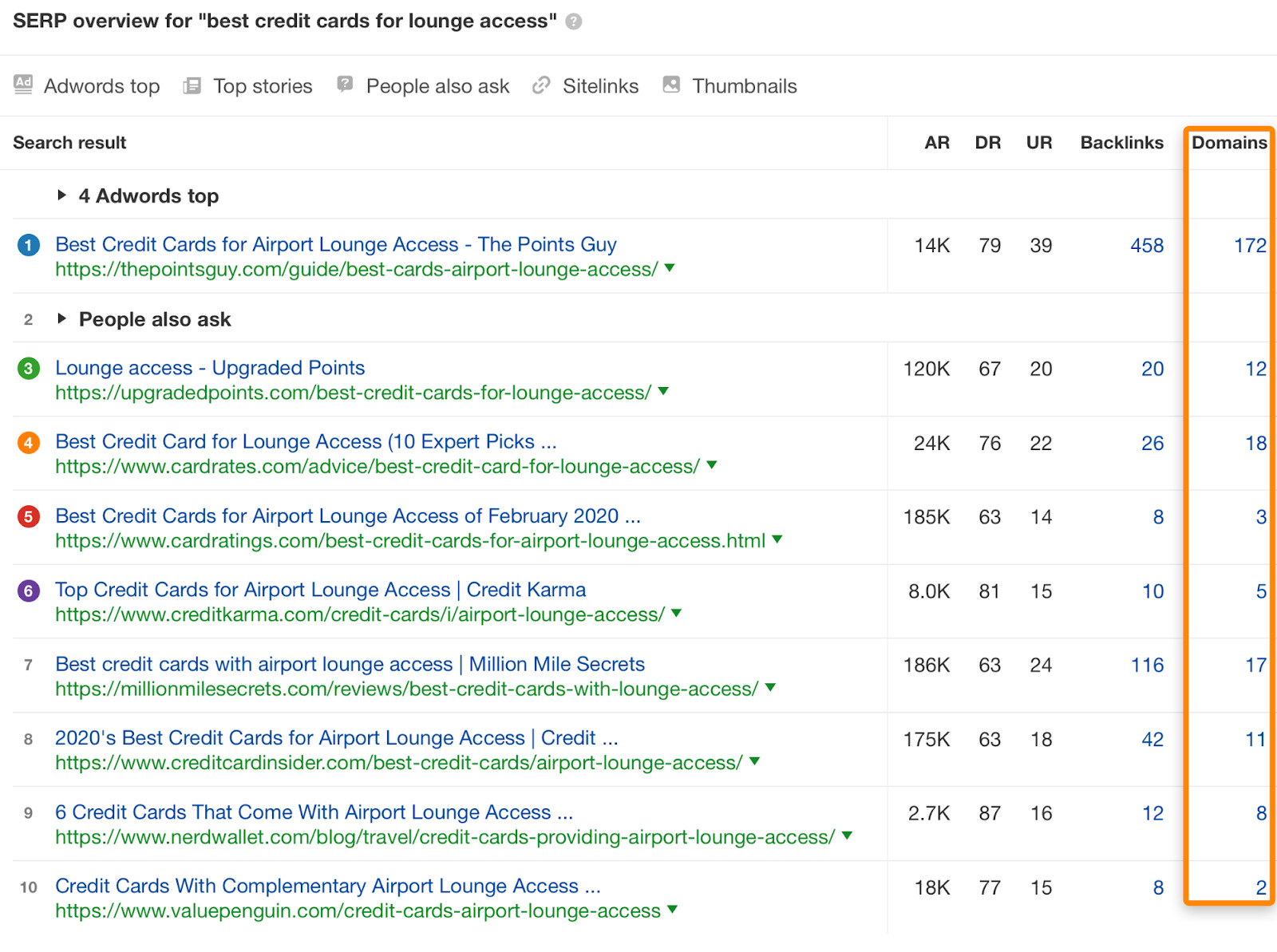

Although the search volume and organic traffic potential may be lower compared to a competitive keyword like "best credit cards," there are also fewer major brands to compete with, and you will not require as many backlinks to rank.
How can you discover easier topics to tackle?
Visit Ahrefs' Keywords Explorer, search for a broad topic, and view the "Phrase match" report. Next, filter for keywords with a low Keyword Difficulty score—anything under 20 is a good starting point.
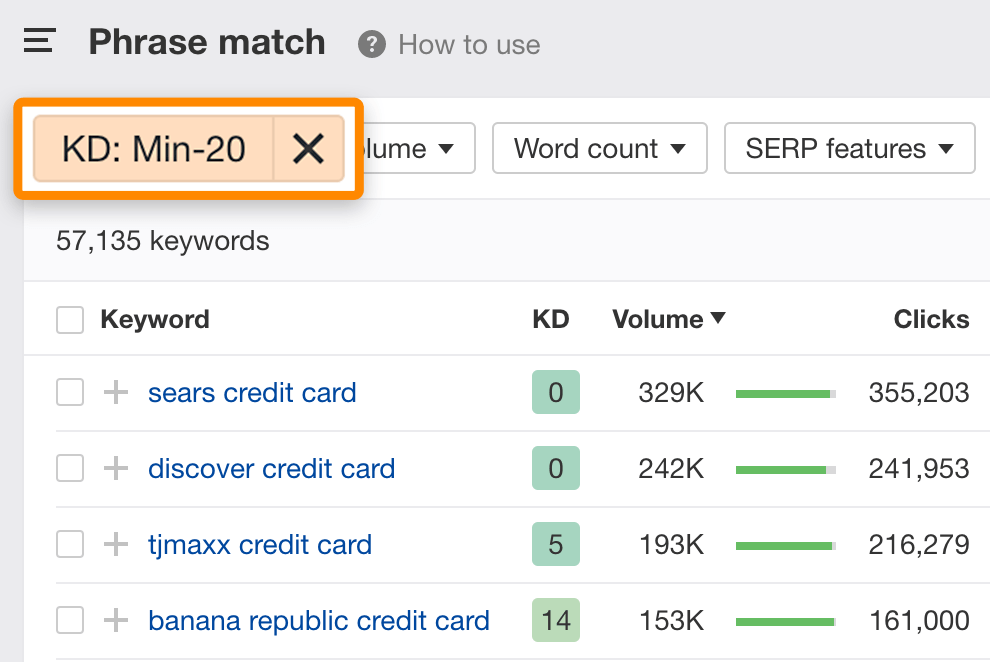

If the suggestions are not highly relevant, use the Include filter to narrow down the results. For example, let us filter the list to include only keywords with the word "best."
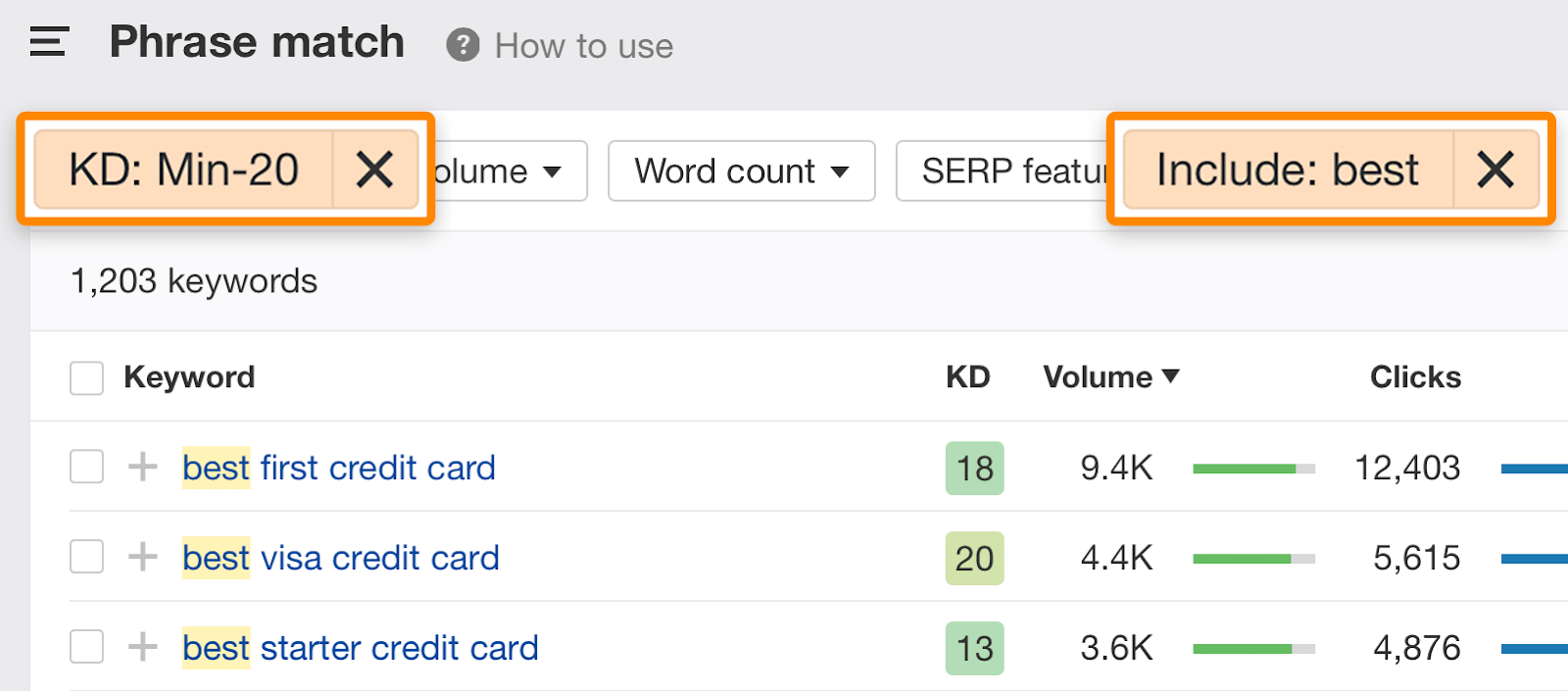

You can then evaluate the SERP to assess the difficulty and competitiveness of the keywords further.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jSOq3ysvBk8
6. Use your target keyword in three strategic locations
Each topic has a "head" keyword, which represents the most common way individuals search for content related to your page.
For a post about natural weight loss, the head keyword would be "natural weight loss":
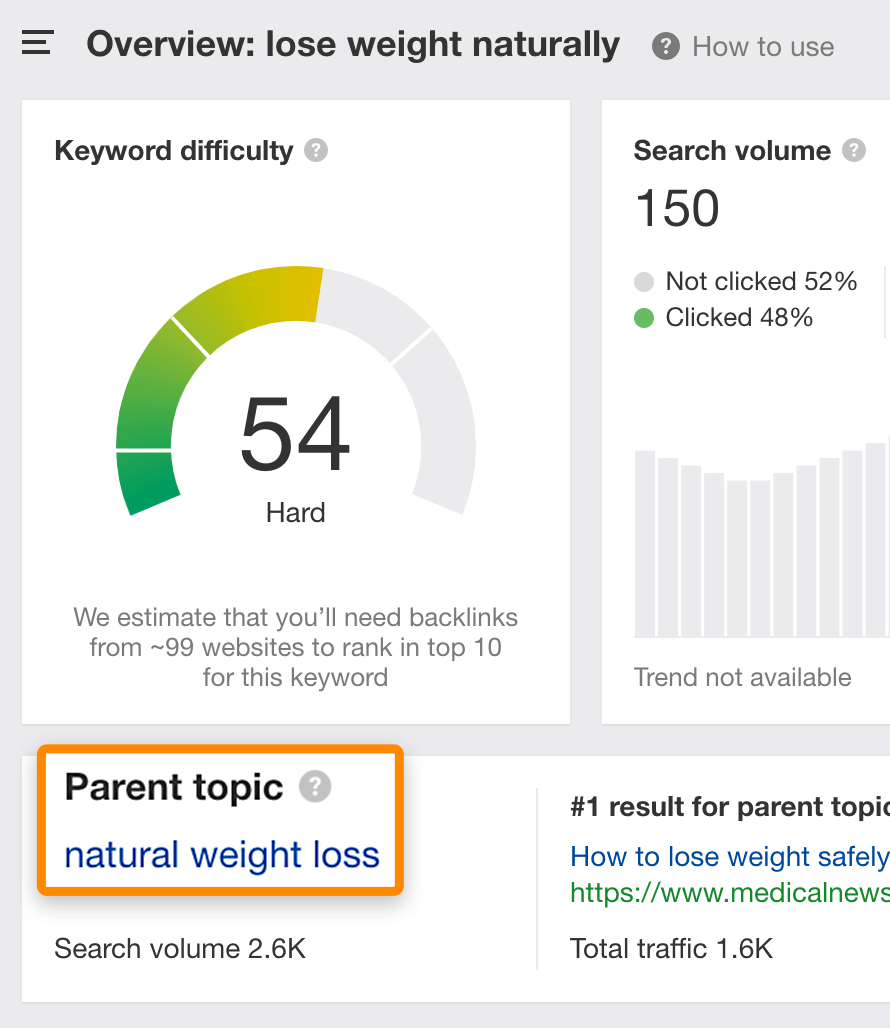

There are three key locations where you should incorporate this keyword:
a) Title tag
Google instructs individuals to write title tags that accurately describe the content of the page. If you are targeting a specific keyword or phrase, the title tag should precisely do that.
This also shows searchers that your page offers the information they want, as it aligns with their query.
While it may not be an extremely important ranking factor, it is still beneficial to include the keyword in the title tag.
That is why we include it in almost all our blog posts:


However, refrain from forcing the keyword into the title tag if it does not make sense. Readability should always be a priority.
For instance, if your target keyword is "kitchen cabinets cheap," it would not make sense as a title tag. Do not hesitate to rearrange the wording or add stop words to ensure clarity—Google is intelligent enough to comprehend your intended meaning.


b) Heading (H1)
Every page should have a visible H1 heading on the page, and it should include your target keyword where it makes sense.


c) URL
Google says to use words in URLs that are relevant to your page’s content.
Using the query you’re targeting is usually the easiest way to do this:

7. Use a short and descriptive URL
Google says to avoid using long URLs because they may intimidate searchers.
For that reason, using the exact target query as the URL isn’t always best practice.
Just imagine that your target keyword is “how to get rid of a tooth abscess without going to the dentist.” Not only is that a mouthful (no pun intended), but it’s also going to get truncated in the search results:


Removing stop words and unnecessary details will give you something shorter and sweeter while keeping the important words.


That said, don’t be afraid to describe your page more succinctly where needed.


Note that if your CMS already has a predefined, ugly URL structure, it’s not a huge deal. And it’s certainly not worth jumping through countless hoops to fix. Google is showing the full URL for fewer and fewer results these days anyway.
Recommended reading: How to Create SEO-Friendly URLs (Step-by-Step)
8. Write a compelling title tag and meta description
Optimizing for search engines isn’t just about improving rankings, but also enticing clicks.
This is why you need to write compelling title tags and meta descriptions because they both show up in search results:


Sidenote.
Google doesn’t always show the defined title and description in the search results. Sometimes they rewrite the title and choose a more appropriate description from the page for the snippet.Your title tag and description are effectively your sales pitch.
If neither of them stands out from the crowd, searchers will click a different result. But beyond including your target keyword, how can you improve CTR?
First, try to keep your title tag under 60 characters, and your descriptions under 150 characters. This helps to avoid truncation.
Second, use title case for titles, and sentence case for descriptions.
Third, align your title and description with search intent.
For instance, almost all of the results for “best headphones” specify the year in their titles and descriptions.
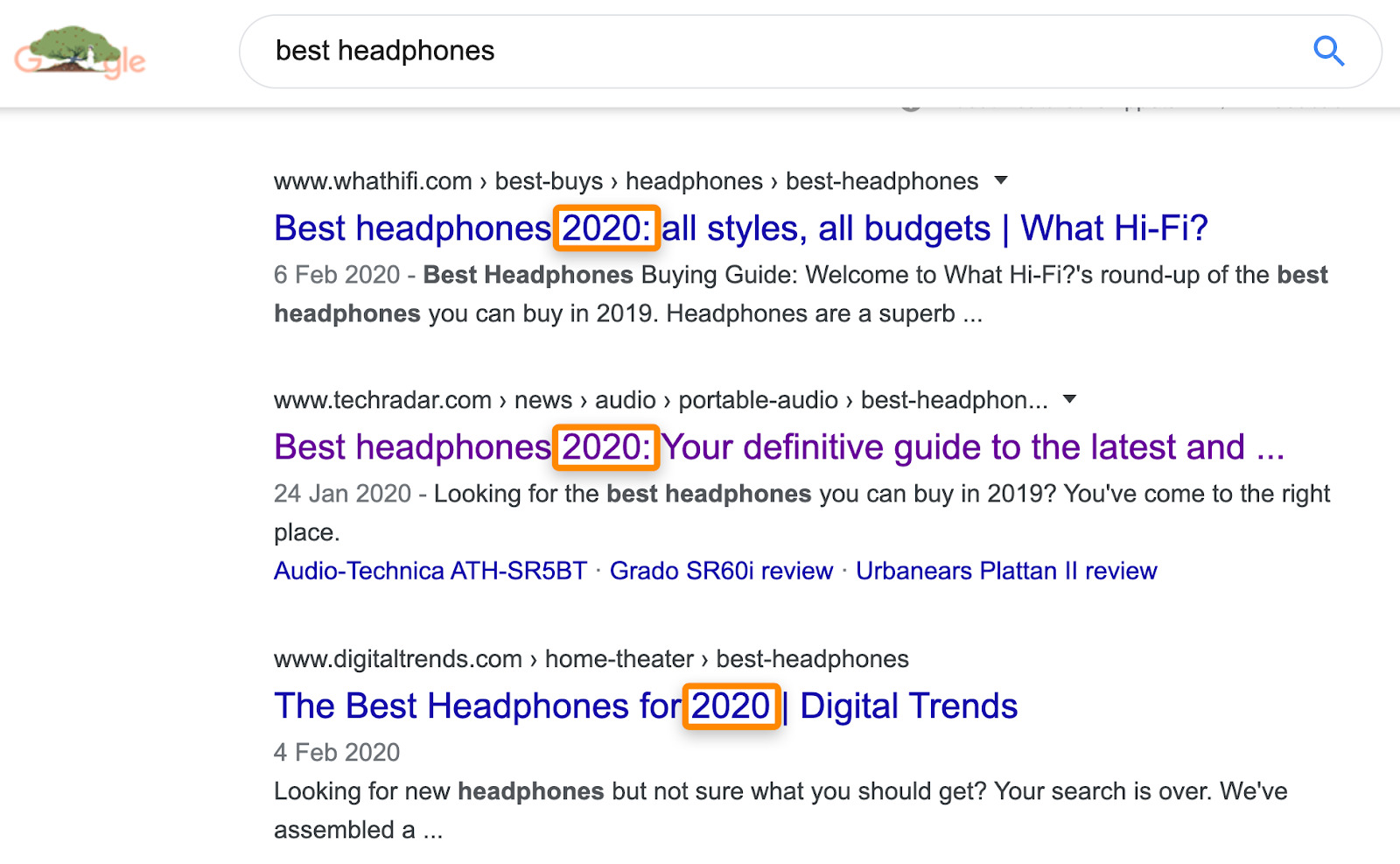

This is because people want lists of up-to-date recommendations, as new headphones are released all the time.
Fourth, use power words to entice the click—without being clickbait-y.

Read more about crafting the perfect title here, or watch this video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jqEoZsIOrYw
Compressing images is vital to ensure fast-loading pages, but this isn’t the only way to optimize images for SEO.
You should also add alt tags and use descriptive filenames.
Both of these things help Google understand your images, which can help your pages rank for long-tail keywords in web search—and in Google Images.
Alt text is extremely helpful for Google Images -- if you want your images to rank there. Even if you use lazy-loading, you know which image will be loaded, so get that information in there as early as possible & test what it renders as.— John (@JohnMu) September 4, 2018
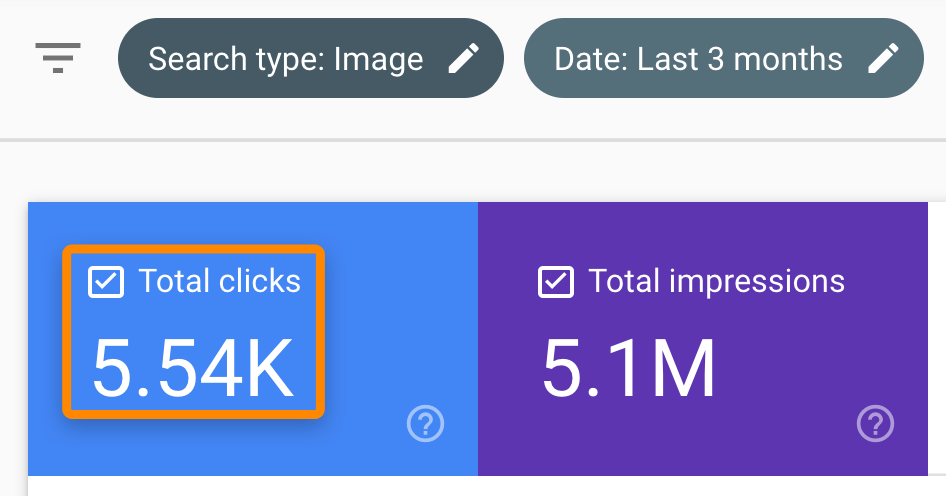
Don’t overlook the importance of Google Images. It’s sent us over 5,500 clicks in the past three months:

Optimizing file names is simple. Just describe your image in words, and separate those words with hyphens.
Here’s an example:


Filename: number-one-handsome-man.jpg
For alt tags, do the same—but use spaces, not hyphens.

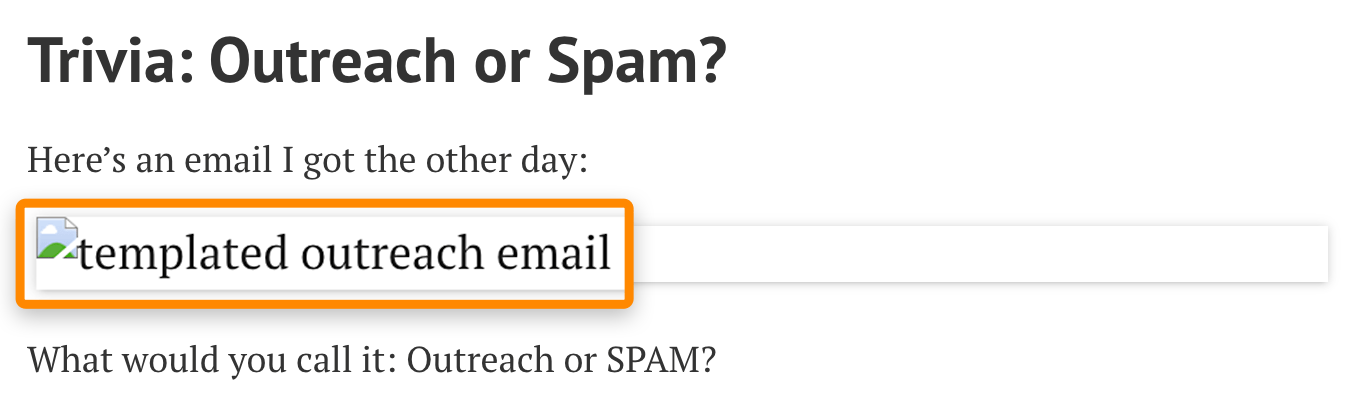
Alt text isn’t only important for Google, but also for visitors.
If an image fails to load, the browser shows the alt tag to explain what the image should have been:

Plus, around 8.1 million Americans have vision impairments and may use a screen reader. These devices read alt tags out loud.
Recommended reading: Image SEO: 12 Actionable Tips (for More Organic Traffic)
10. Write thorough content
Earlier, we mentioned that search volume isn’t always a good predictor of organic traffic potential because many pages also get traffic from long-tail queries.
For instance, this page ranks #1 for “best laptop brands”…
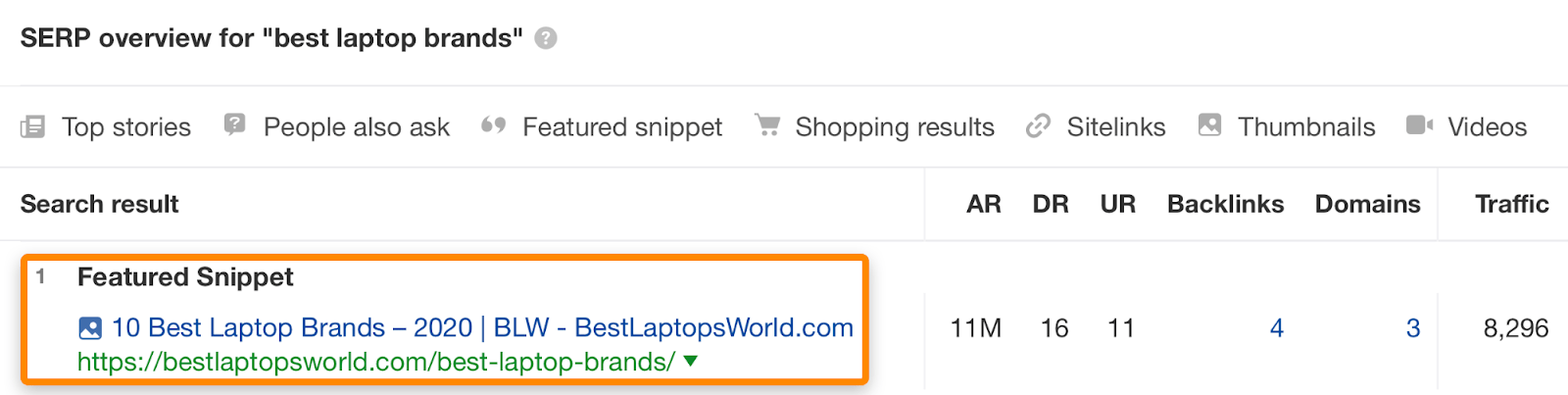

… but it also ranks in the top 10 for over 300 other keywords like “best computer brands” and “is lenovo a good brand”:
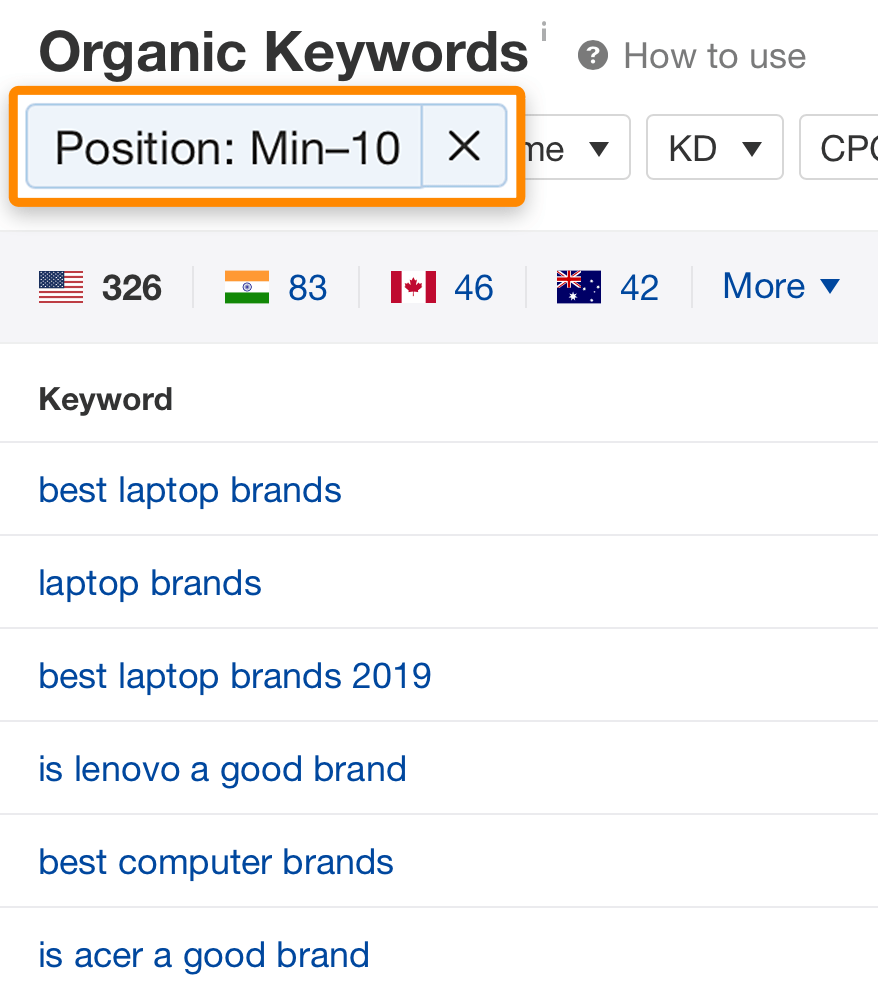

This isn’t abnormal.
Our study of three million search queries found that the average top-ranking page ranks in the top 10 for almost 1,000 other keywords.
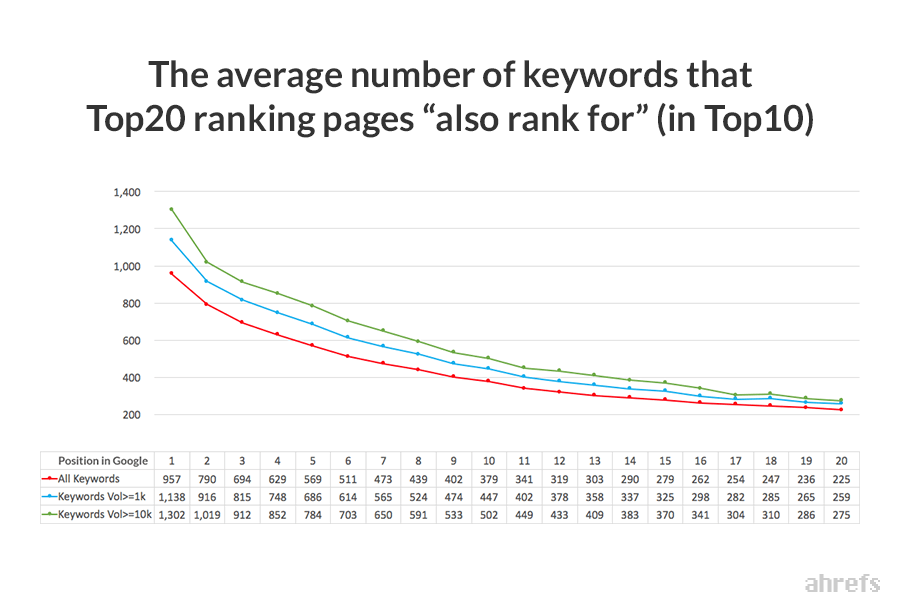

How do you rank for more queries? Make your content more thorough.
Note that this isn’t about content length, but covering relevant subtopics that people are also searching for. It applies mainly to informational SEO content like blog posts but can help other types of content too.
Here are three ways to find subtopics:
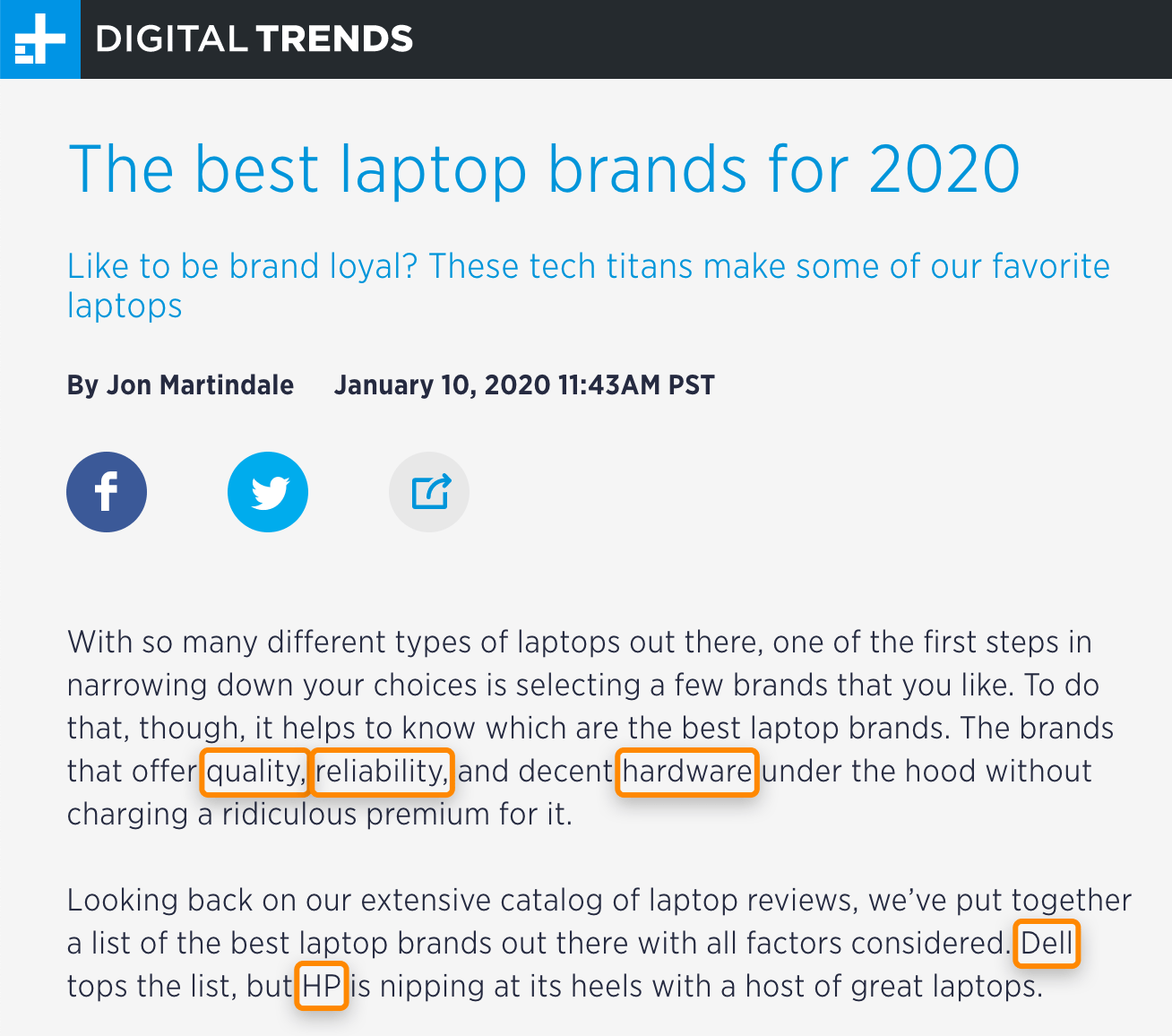
a) Look for relevant keywords on the top-ranking pages
If we look at one of the top-ranking pages for “best laptop brands,” we see relevant keywords like “dell,” “hp,” “quality,” “reliability,” and “hardware.”

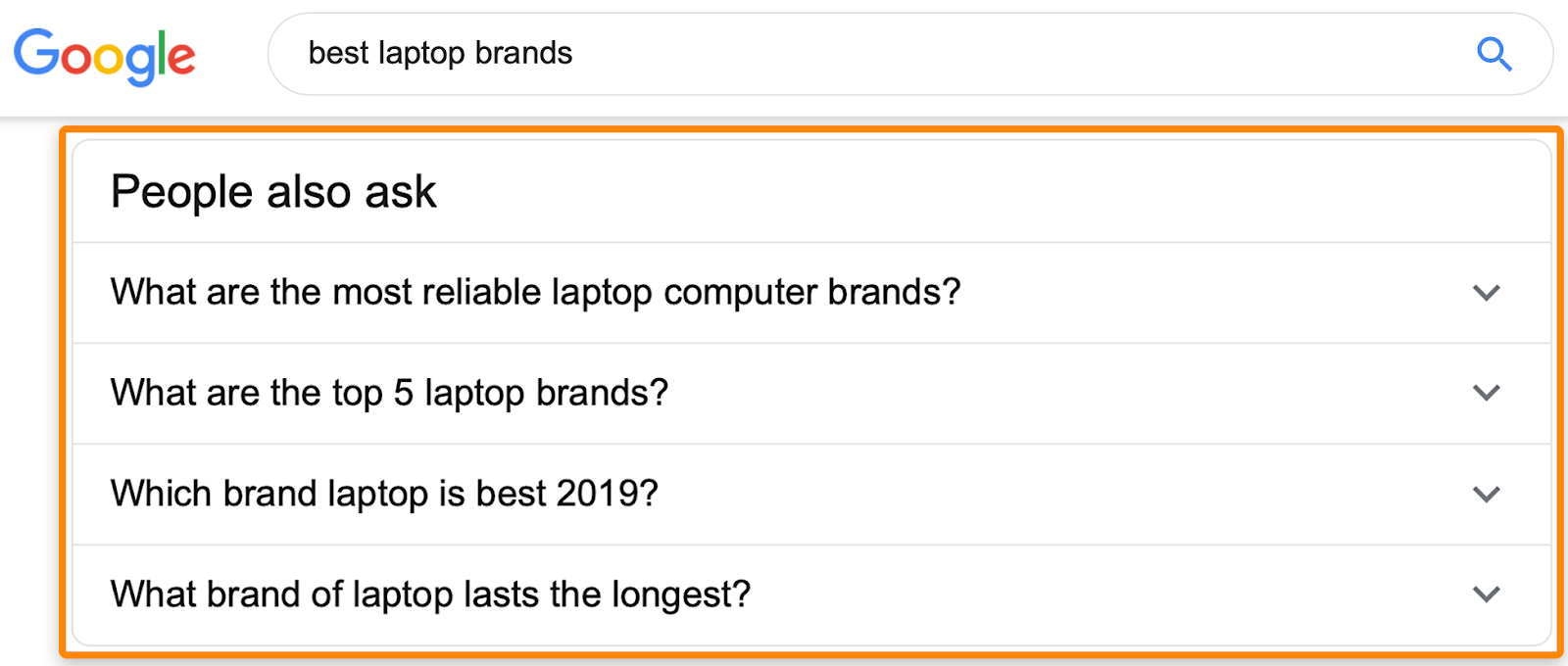
b) Look at “People also ask” results
For “best laptop brands,” we see a couple of reliability-related questions.

c) Run a Content Gap analysis
Paste the URLs of three top-ranking pages into Ahrefs’ Content Gap tool. Leave the bottom field blank and hit “Show keywords.”
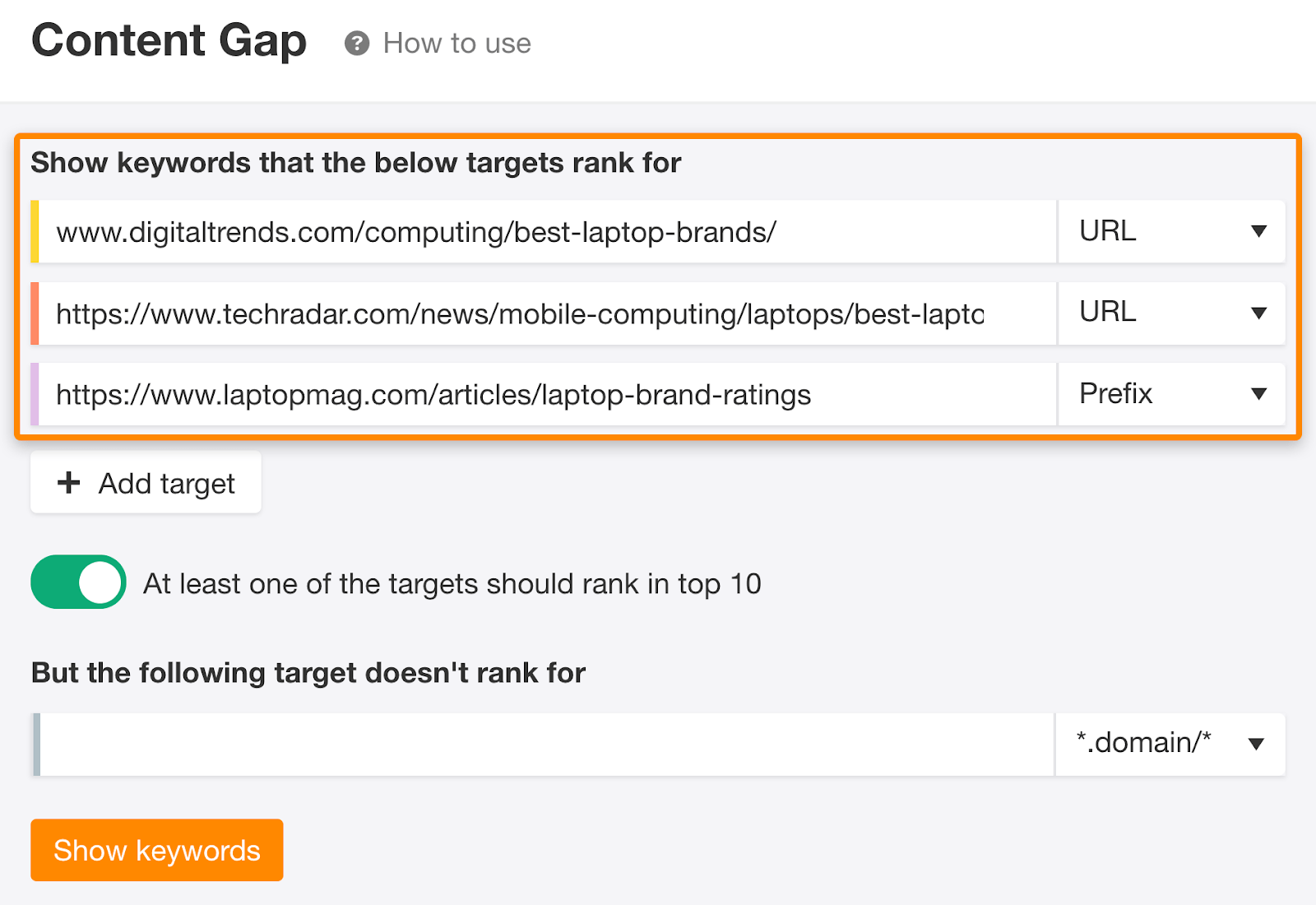

This shows queries that one or more of the top-ranking pages also rank for.
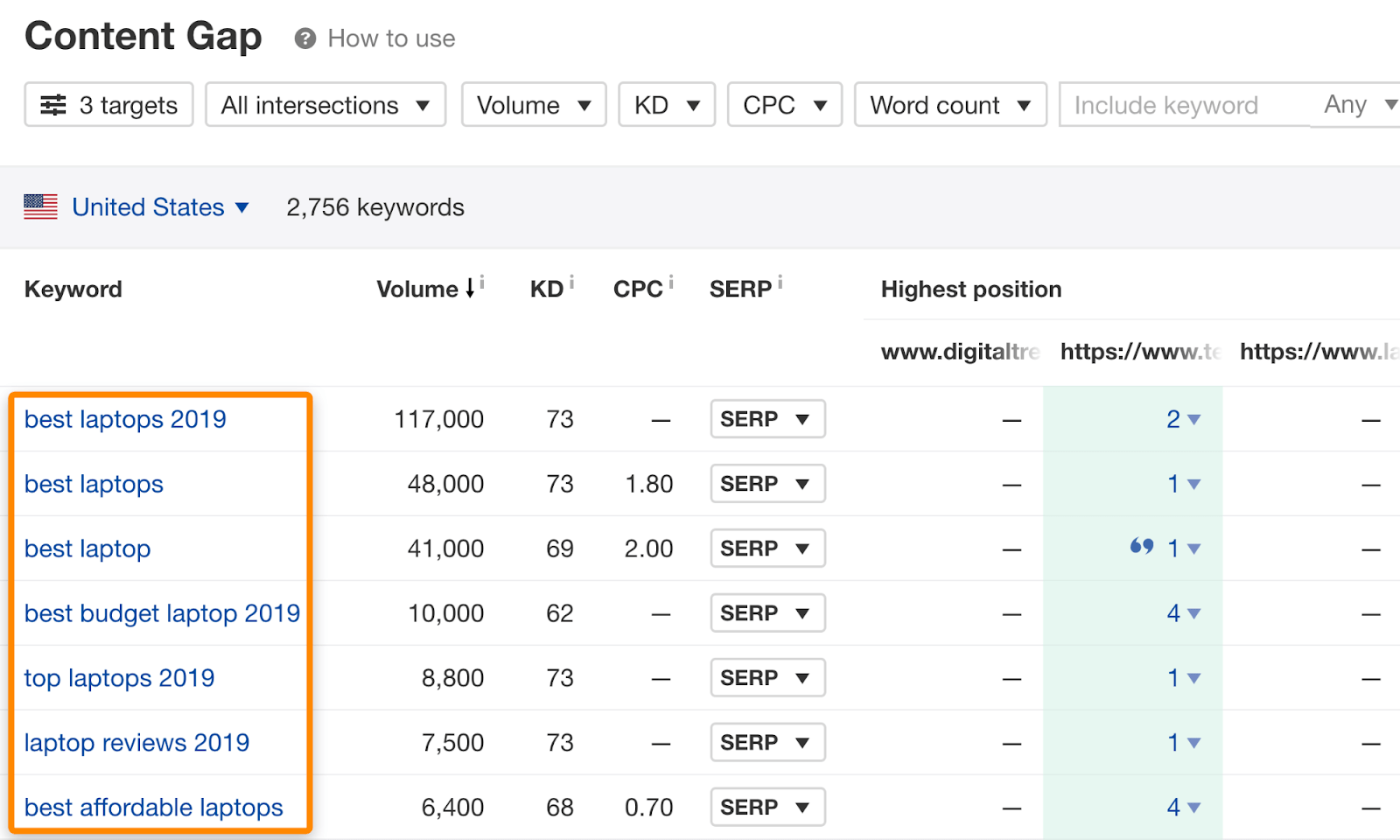

Turn off intersections one and two to refine results further.
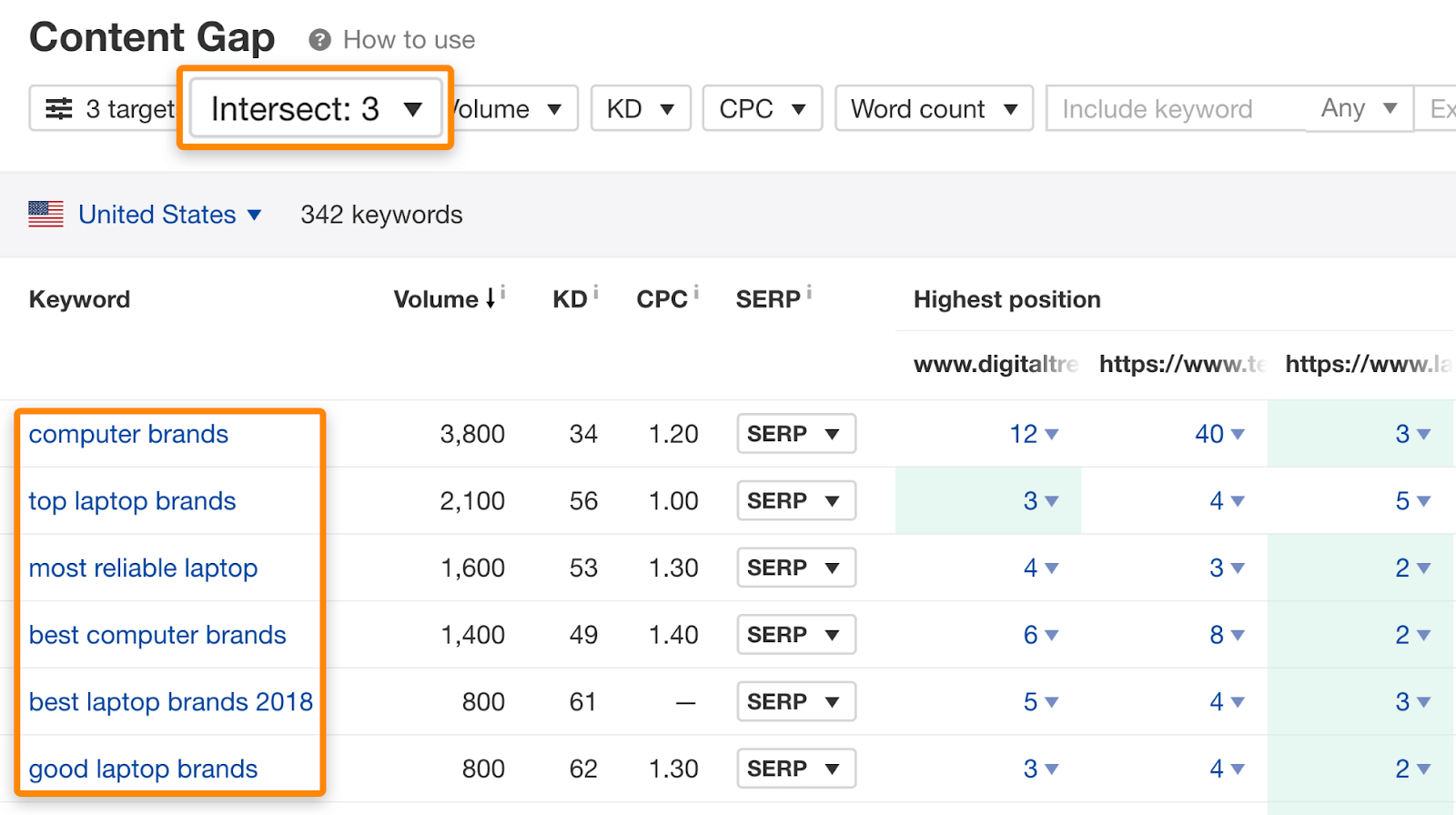

11. Add internal links from other relevant pages
Internal links are those from one page on your website to another.
Generally speaking, the more links a page has—from both external and internal sources—the higher its PageRank. This is the foundation of Google’s ranking algorithm and remains important even today.
DYK that after 18 years we’re still using PageRank (and 100s of other signals) in ranking?
Wanna know how it works?https://t.co/CfOlxGauGF pic.twitter.com/3YJeNbXLml— Gary “鯨理/경리” Illyes (@methode) February 9, 2017
Unfortunately, Google discontinued public PageRank scores in 2016, so there’s no way to check them anymore. However, Ahrefs’ URL Rating is a similar metric, and it correlates with rankings.
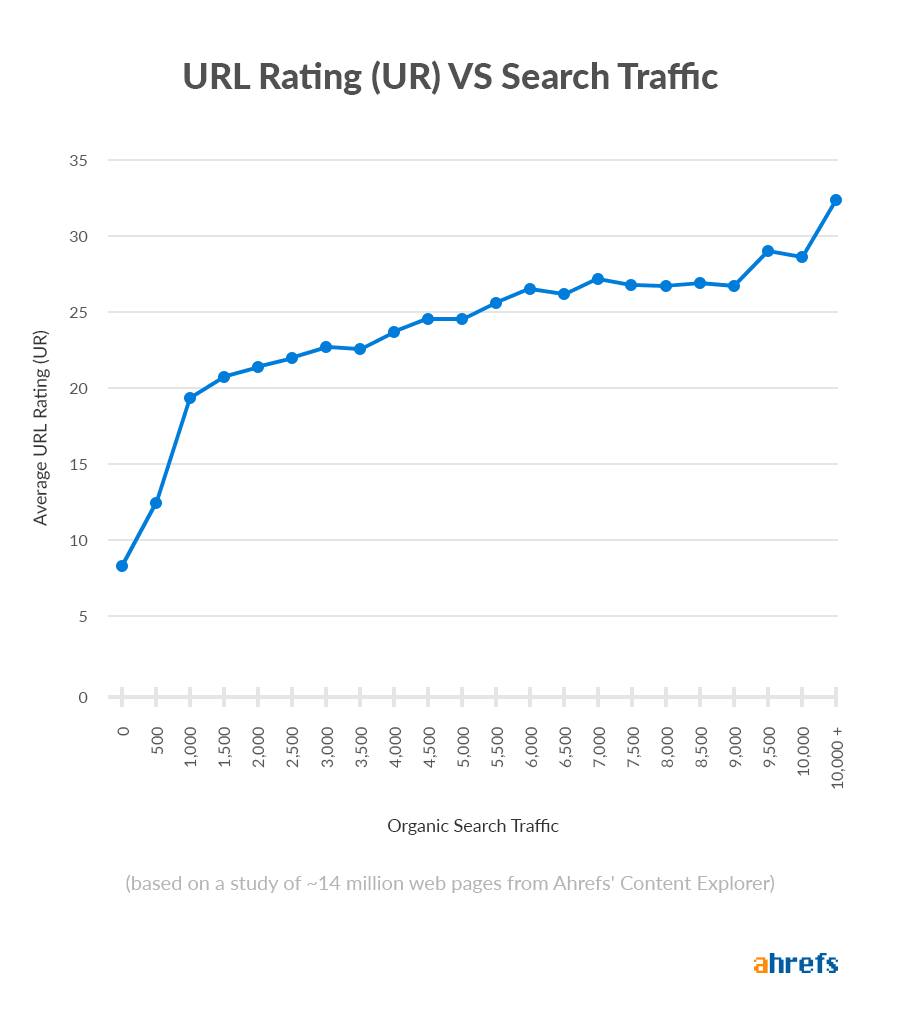

Internal links also help Google understand what a page is about.
Most links do provide a bit of additional context through their anchor text. At least they should, right‽— John (@JohnMu) November 23, 2017
Luckily, most CMS’ add internal links to new web pages from at least one other page by default. This might be on the menu bar, on the blog homepage, or somewhere else.
However, it’s good practice to add internal links from other relevant pages whenever you publish something new.
To do that, run a search in Google for site:yourdomain.com [page topic]
This will return the most relevant pages on your site about that topic:
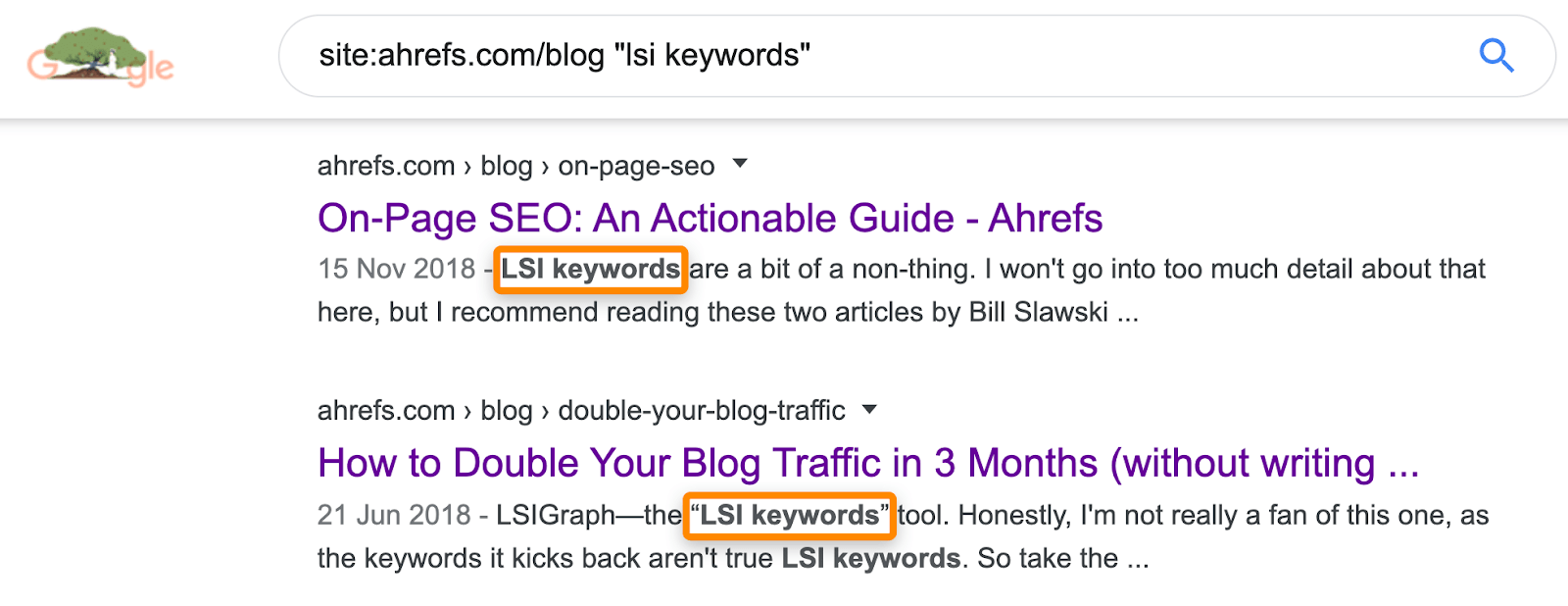

Look for suitable places to add internal links on pages that fit the bill.
You can also find internal link opportunities in Ahrefs’ Site Explorer. Paste in your domain, then go to the “Best by Links” report. This shows you all the pages on your site sorted by URL Rating:
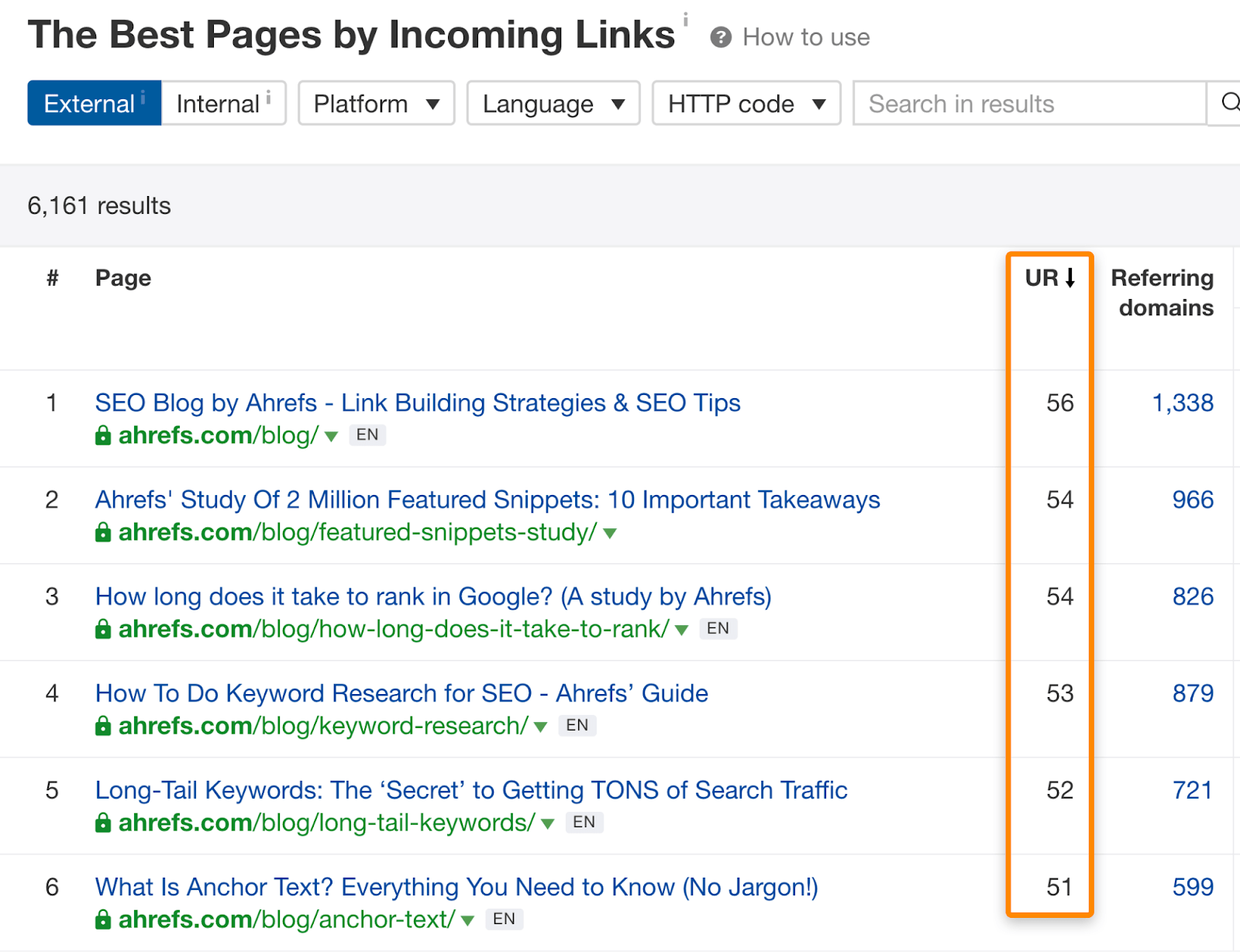

Look for relevant pages and add internal links where appropriate.
Recommended reading: Internal Links for SEO: An Actionable Guide
Backlinks are the foundation of Google’s algorithm and remain one of the most important ranking factors.
Google confirms this on their “how search works” page, where they say:
If other prominent websites on the subject link to the page, that’s a good sign that the information is of high quality.
But don’t take Google’s word for it…
Our study of over one billion web pages shows a clear correlation between organic traffic and the number of websites linking to a page:
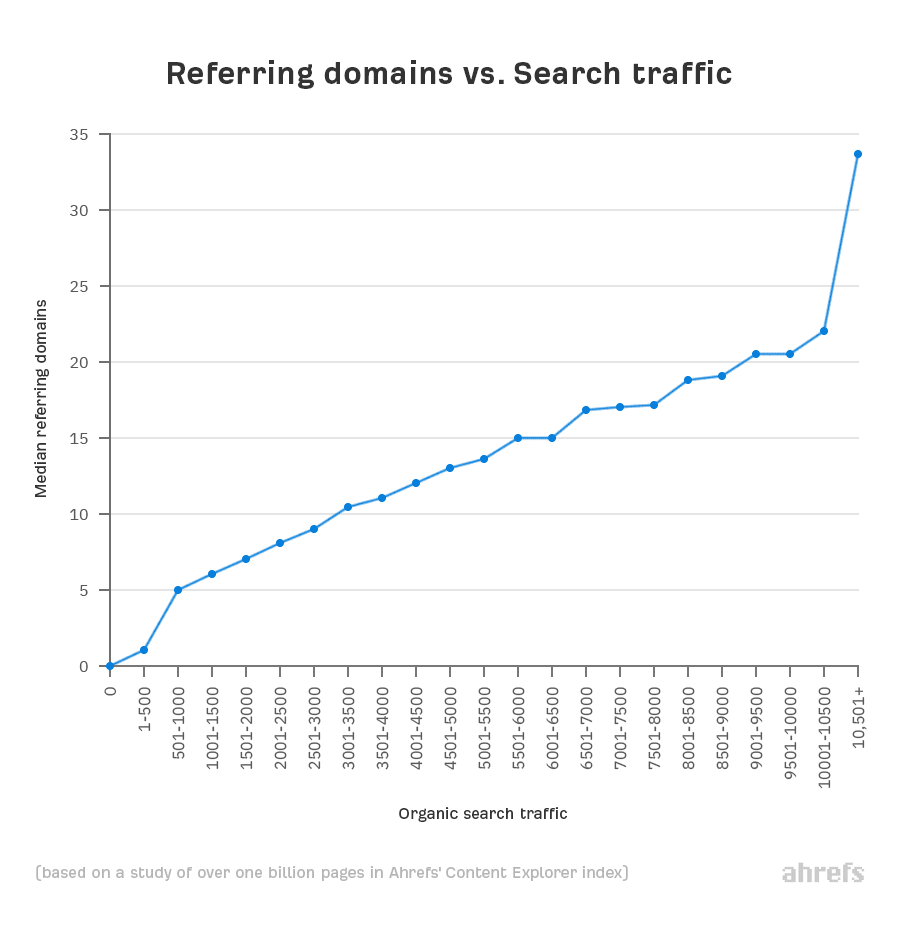

Just remember that this is about quality, not just quantity.
You should aim to build backlinks from authoritative and relevant pages and websites.
Read more about what makes a good backlink here, or watch this video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E3mDlVutW_o
Final thoughts
Best practices are a good starting point, but they’re not always enough to rank. There are other important ranking factors to keep in mind and other ways to improve SEO.
Read this post if you’re still struggling to rank higher, or watch this video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rm1MbJneLSI
Source

